Chapter 44
Excitement
People Affected: everyone
Type of Emotion: sensory reward
Sensory Trigger: new scenery
Mental Effect: positive
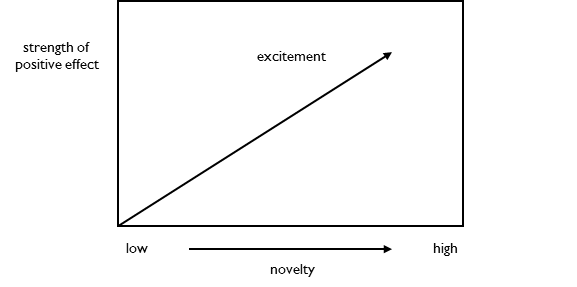
Key Feature: the more novel the scenery, the stronger the effect
Key Feature: effect generally stronger in men
Type of Emotion: sensory reward
Sensory Trigger: new scenery
Mental Effect: positive
Key Feature: the more novel the scenery, the stronger the effect
Key Feature: effect generally stronger in men
Purpose
Excitement encourages everyone to explore for new scenery.
Exploring for new scenery helps your group, but harms you and your genes.
Your group has a lot to gain and little to lose. If you find new territory that is habitable, your group headcount can be increased for an infinite number of generations. If you die, you are replaced in one generation.
You and your genes either lose a little or lose a lot. At best, you waste time exploring that could have been used to gather more food or reproduce more. At worst, you die and your reproduction stops.
Sensory Trigger
Excitement is triggered by new scenery. Vacations and weekend trips trigger excitement. The countryside is exciting to urbanites. The city is exciting to farmers. Everyone feels excitement the first time they visit Las Vegas.
Excitement is mistakenly triggered by a change of weather or season. The changing of the leaves and the first snowfall trigger excitement. Christmas decorations also trigger excitement for the first week.
Excitement is also mistakenly triggered by postcards, magazines, television and kaleidoscopes.
Excitement is not triggered by anticipating positive emotions. If someone says they are excited about being promoted, they are anticipating the positive effect of pride.
Curiosity is the desire to trigger excitement. The desire to see what lays around the corner or over the hill is the desire to feel the excitement triggered by a new vista.
Mental Effect
Excitement encourages everyone to explore for new scenery.
Exploring for new scenery helps your group, but harms you and your genes.
Your group has a lot to gain and little to lose. If you find new territory that is habitable, your group headcount can be increased for an infinite number of generations. If you die, you are replaced in one generation.
You and your genes either lose a little or lose a lot. At best, you waste time exploring that could have been used to gather more food or reproduce more. At worst, you die and your reproduction stops.
Sensory Trigger
Excitement is triggered by new scenery. Vacations and weekend trips trigger excitement. The countryside is exciting to urbanites. The city is exciting to farmers. Everyone feels excitement the first time they visit Las Vegas.
Excitement is mistakenly triggered by a change of weather or season. The changing of the leaves and the first snowfall trigger excitement. Christmas decorations also trigger excitement for the first week.
Excitement is also mistakenly triggered by postcards, magazines, television and kaleidoscopes.
Excitement is not triggered by anticipating positive emotions. If someone says they are excited about being promoted, they are anticipating the positive effect of pride.
Curiosity is the desire to trigger excitement. The desire to see what lays around the corner or over the hill is the desire to feel the excitement triggered by a new vista.
Mental Effect
Excitement varies with novelty. The more novel scenery is, the stronger the positive effect. Foreign cities trigger more excitement than domestic cities.
Pleasing Scenery and Excitement
Pleasing Scenery and Excitement
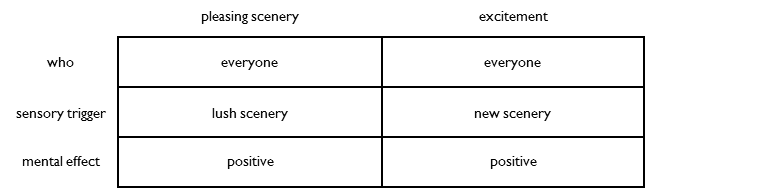
Pleasing scenery and excitement are similar, but different sensations. Pleasing scenery is triggered by lush scenery, whether it is new or not. Excitement is triggered by new scenery, whether it is lush or not.
Pleasing scenery and excitement serve different purposes. Pleasing scenery encourages living near food. Excitement encourages finding new territory.
The most enjoyable scenery is lush and new, which triggers both sensations.
Pleasing scenery and excitement serve different purposes. Pleasing scenery encourages living near food. Excitement encourages finding new territory.
The most enjoyable scenery is lush and new, which triggers both sensations.
Happiness Dissected is a more practical version of The Origin of Emotions.