Chapter 49
Involuntary Expressions
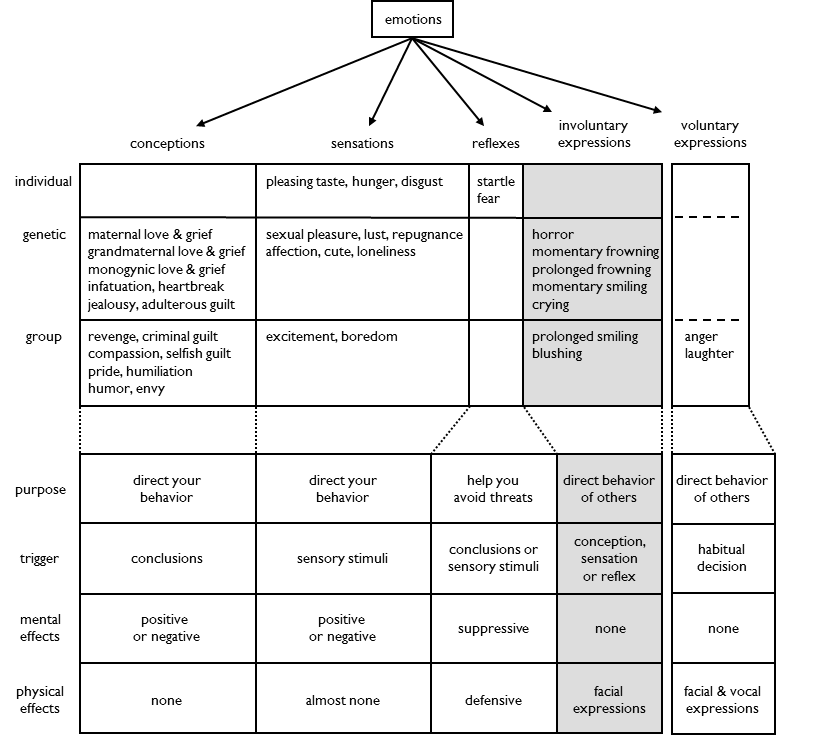
Involuntary
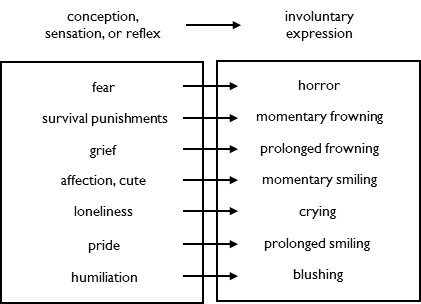
expressions are triggered by a conception, sensation or reflex.
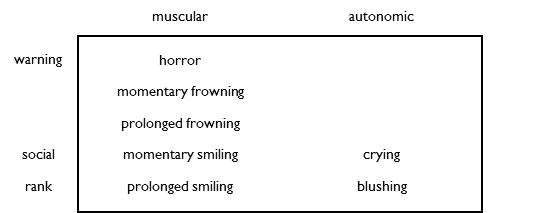
There are two types of involuntary expression: muscular and autonomic.
Muscular expressions use facial muscles. There are three basic muscular expressions: horror, frowning and smiling. Prolonged frowning and prolonged smiling are just extended versions of two basic expressions.
Muscular expressions evolved during our aquatic detour. We used facial expressions to communicate underwater. We are the only primates that smile or frown. We are also the only primates that have eyebrows, white eyes or chins.
Autonomic expressions use autonomic systems. Crying uses the tear glands. Blushing uses the circulatory system.
Autonomic expressions evolved after our aquatic detour. Crying is a re-adaptation of a mechanism previously used to leak salt. Blushing evolved after our three color vision evolved a second time. Three color vision, which is required to see blushing, is only used by terrestrial species.
Involuntary expressions fall into three categories of purpose: warning, social and rank.
Muscular expressions use facial muscles. There are three basic muscular expressions: horror, frowning and smiling. Prolonged frowning and prolonged smiling are just extended versions of two basic expressions.
Muscular expressions evolved during our aquatic detour. We used facial expressions to communicate underwater. We are the only primates that smile or frown. We are also the only primates that have eyebrows, white eyes or chins.
Autonomic expressions use autonomic systems. Crying uses the tear glands. Blushing uses the circulatory system.
Autonomic expressions evolved after our aquatic detour. Crying is a re-adaptation of a mechanism previously used to leak salt. Blushing evolved after our three color vision evolved a second time. Three color vision, which is required to see blushing, is only used by terrestrial species.
Involuntary expressions fall into three categories of purpose: warning, social and rank.
Warning expressions warn kin about harm. Horror warns kin about threats. Momentary frowning warns kin about toxins or trauma. Prolonged frowning warns kin about grief by making it tangible.
Social expressions encourage kin to interact with you. Momentary smiling triggers affection in kin, which rewards them for interacting with you. Crying triggers compassion in kin, which they stop by interacting with you.
Rank expressions encourage others to increase their rank or to not reduce yours. Prolonged smiling makes the reward of pride tangible to others. Blushing triggers compassion in others, which they stop by not laughing at you.
Involuntary expressions only help your genes or your group. If an expression helps you, you express it voluntarily.
Involuntary expressions only help your genes or your group. If an expression helps you, you express it voluntarily.
Happiness Dissected is a more practical version of The Origin of Emotions.