Chapter 2
Five Types of Emotion
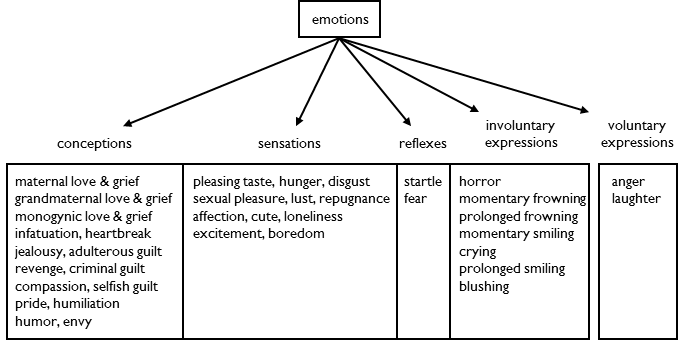
There are five types of emotion: conceptions, sensations, reflexes, involuntary expressions and voluntary expressions.
Conceptions, sensations, reflexes and involuntary expressions are biological adaptations. They are transmitted to the next generation through reproduction. They are universal to the species.
Voluntary expressions are cultural adaptations. They are transmitted to the next generation through interaction. They vary by culture.
Conceptions, sensations, reflexes and involuntary expressions are biological adaptations. They are transmitted to the next generation through reproduction. They are universal to the species.
Voluntary expressions are cultural adaptations. They are transmitted to the next generation through interaction. They vary by culture.
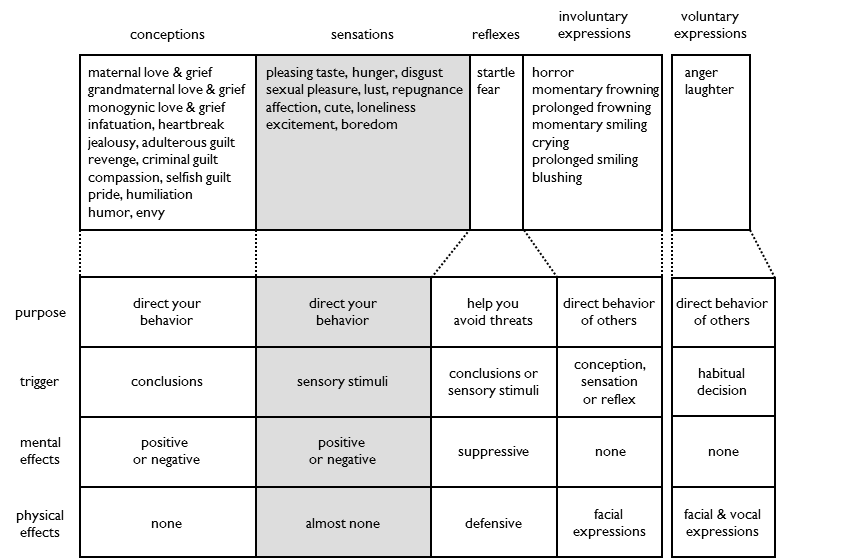
Conceptions direct your behavior.
Conceptions are positive or negative mental effects that are triggered by conclusions.
Maternal love is a positive effect triggered by the conclusion “my child is happy”. Maternal grief is a negative effect triggered by the conclusion “my child is dead”.
Conceptions can also be triggered by imagining a conclusion. Maternal grief can be triggered by imagining the conclusion “my child is dead”.
Conceptions do not trigger physical effects. Conceptions do not need to trigger physical effects to direct your behavior.
A few conceptions do trigger involuntary expressions, which have a different purpose.
Conceptions are positive or negative mental effects that are triggered by conclusions.
Maternal love is a positive effect triggered by the conclusion “my child is happy”. Maternal grief is a negative effect triggered by the conclusion “my child is dead”.
Conceptions can also be triggered by imagining a conclusion. Maternal grief can be triggered by imagining the conclusion “my child is dead”.
Conceptions do not trigger physical effects. Conceptions do not need to trigger physical effects to direct your behavior.
A few conceptions do trigger involuntary expressions, which have a different purpose.
Sensations direct your behavior.
Sensations are positive or negative mental effects that are triggered by the presence or absence of sensory stimuli.
Pleasing taste is a positive effect triggered by the taste of food. Hunger is a negative effect triggered by the absence of food. Disgust is a negative effect triggered by the smell of toxins, such as fecal matter.
Sensations can be triggered by stimuli that is real, recorded, remembered or imagined. Men feel sexual pleasure when they see a naked woman whether she is real, recorded, remembered or imagined.
Sensations trigger almost no physical effects. A few sensations do trigger minor physical effects, like salivation. However, sensations do not trigger any major physical effects, like increased heart rate. Sensations do not need to trigger physical effects to direct your behavior.
A few sensations do trigger involuntary expressions, which have a different purpose.
Sensations are positive or negative mental effects that are triggered by the presence or absence of sensory stimuli.
Pleasing taste is a positive effect triggered by the taste of food. Hunger is a negative effect triggered by the absence of food. Disgust is a negative effect triggered by the smell of toxins, such as fecal matter.
Sensations can be triggered by stimuli that is real, recorded, remembered or imagined. Men feel sexual pleasure when they see a naked woman whether she is real, recorded, remembered or imagined.
Sensations trigger almost no physical effects. A few sensations do trigger minor physical effects, like salivation. However, sensations do not trigger any major physical effects, like increased heart rate. Sensations do not need to trigger physical effects to direct your behavior.
A few sensations do trigger involuntary expressions, which have a different purpose.
Reflexes help you avoid threats.
Reflexes are triggered by conclusions or sensory stimuli. Fear can be triggered by the conclusion “a man is pointing a loaded gun at me”. Fear can also be triggered by the sight of a snake.
Reflexes trigger a mental effect that suppresses conceptions and sensations. When you are frightened, you cannot feel sexual pleasure or humiliation. Suppression helps you concentrate on avoiding a threat by eliminating distractions.
Reflexes trigger defensive physical effects. Startle involuntarily tenses neck muscles, which prevents tearing by a predator’s claws or talons. Fear releases adrenalin to increase heart rate, which helps fight or flight.
Reflexes are the only emotions that trigger major physical effects.
Reflexes are triggered by conclusions or sensory stimuli. Fear can be triggered by the conclusion “a man is pointing a loaded gun at me”. Fear can also be triggered by the sight of a snake.
Reflexes trigger a mental effect that suppresses conceptions and sensations. When you are frightened, you cannot feel sexual pleasure or humiliation. Suppression helps you concentrate on avoiding a threat by eliminating distractions.
Reflexes trigger defensive physical effects. Startle involuntarily tenses neck muscles, which prevents tearing by a predator’s claws or talons. Fear releases adrenalin to increase heart rate, which helps fight or flight.
Reflexes are the only emotions that trigger major physical effects.
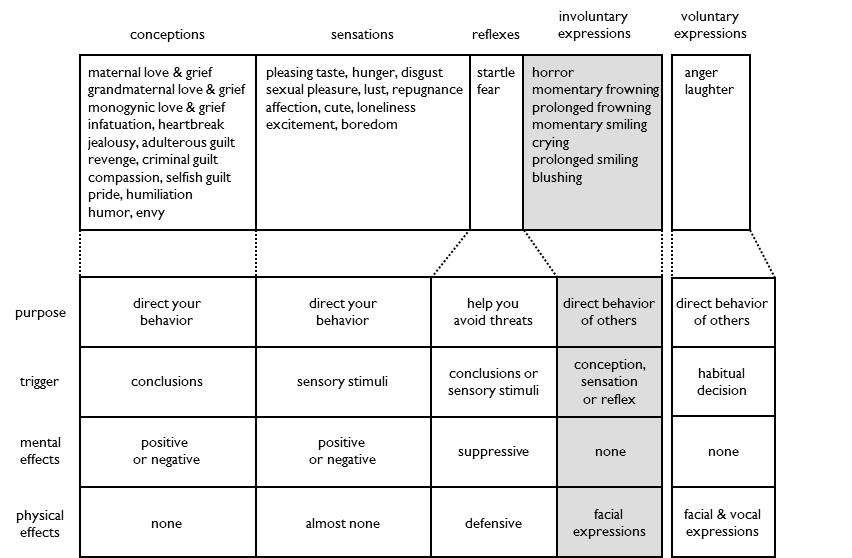
Involuntary expressions direct the behavior of others.
Involuntary expressions are triggered by a conception, sensation or reflex. The reflex of fear triggers the involuntary expression of horror.
Involuntary expressions have a different purpose than their trigger emotion. Fear helps you avoid threats. The expression of horror on your face helps others avoid threats.
Involuntary expressions are triggered by a conception, sensation or reflex. The reflex of fear triggers the involuntary expression of horror.
Involuntary expressions have a different purpose than their trigger emotion. Fear helps you avoid threats. The expression of horror on your face helps others avoid threats.
Voluntary expressions direct the behavior of others.
Voluntary expressions are triggered by habitual decision. Anger is a habitual response to feeling revenge. Laughter is a habitual response to feeling humor. These expressions seem involuntary because they are deeply ingrained habits, like walking or talking.
Voluntary expressions are better than speech. Anger is more credible than calmly stating “I am being coerced by revenge to harm you”. Laughter can be understood more easily than an audience of people simultaneously saying “I feel humor”.
Voluntary expressions are triggered by habitual decision. Anger is a habitual response to feeling revenge. Laughter is a habitual response to feeling humor. These expressions seem involuntary because they are deeply ingrained habits, like walking or talking.
Voluntary expressions are better than speech. Anger is more credible than calmly stating “I am being coerced by revenge to harm you”. Laughter can be understood more easily than an audience of people simultaneously saying “I feel humor”.
Happiness Dissected is a more practical version of The Origin of Emotions.