Chapter 50
Horror
People Affected: everyone
Type of Emotion: muscular involuntary expression
Trigger Emotion: fear
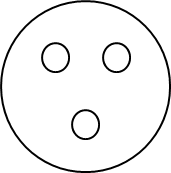
Facial Expression: three circles formed by the eyebrows and mouth
Facial Expression: eyelids open wide to fully show whites of eyes
Key Feature: can be triggered at birth
Type of Emotion: muscular involuntary expression
Trigger Emotion: fear
Facial Expression: three circles formed by the eyebrows and mouth
Facial Expression: eyelids open wide to fully show whites of eyes
Key Feature: can be triggered at birth
Purpose
Horror helps kin avoid threats. If kin see you express horror, they have extra time to avoid the threat that triggered your fear.
Horror also helps groups. If your co-workers or friends see you express horror, your expression helps non-kin avoid a threat.
Facial Expression
Horror helps kin avoid threats. If kin see you express horror, they have extra time to avoid the threat that triggered your fear.
Horror also helps groups. If your co-workers or friends see you express horror, your expression helps non-kin avoid a threat.
Facial Expression
Horror is forming three circles with the eyebrows and mouth. The bottom of the eye sockets form the bottoms of the top circles. Edvard Munch’s The Scream is an example.
Horror triggers sensory fear in others. You feel slight sensory fear when you look at the diagram above.
Horror is the most visible expression. Horror visibly distorts the face more than the other expressions.
Other Species
Most animals that live in groups have a predator warning expression. Most predator warnings are vocal expressions. Unlike facial expressions, vocal expressions do not require line-of-sight and close proximity. A screaming squirrel warns more squirrels than a squirrel with a horrified look on its face.
Eyebrows
Eyebrows evolved solely for communication. Eyebrows do not protect your eyes. The skeletal bump underneath eyebrows does protect your eyes, but not the hair on it. Eyebrows are equivalent to canine tails.
Only humans have eyebrows, which were used to communicate underwater during our aquatic detour.
Horror triggers sensory fear in others. You feel slight sensory fear when you look at the diagram above.
Horror is the most visible expression. Horror visibly distorts the face more than the other expressions.
Other Species
Most animals that live in groups have a predator warning expression. Most predator warnings are vocal expressions. Unlike facial expressions, vocal expressions do not require line-of-sight and close proximity. A screaming squirrel warns more squirrels than a squirrel with a horrified look on its face.
Eyebrows
Eyebrows evolved solely for communication. Eyebrows do not protect your eyes. The skeletal bump underneath eyebrows does protect your eyes, but not the hair on it. Eyebrows are equivalent to canine tails.
Only humans have eyebrows, which were used to communicate underwater during our aquatic detour.
Happiness Dissected is a more practical version of The Origin of Emotions.